
Massage
Therapy
Boris Stone - Outrageously Active Recovery
Using different types of Massage Therapy will help aid your recovery after injury or help you to function better in your sports or activities of daily living.
During the Functional Assessment, clients are assessed, which leads to suitable treatment and a follow-up treatment plan to help prevent and recover from injuries.


Soft tissue therapy can significantly aid in the recovery from musculoskeletal injuries by promoting blood circulation, reducing muscle tension, and enhancing tissue elasticity.
This therapy targets muscles, tendons, and ligaments, helping to break down scar tissue and adhesions that can limit movement and cause pain.
By relieving tightness and improving flexibility and mobility, soft tissue therapy can restore normal function and accelerate healing.
Additionally, it can reduce inflammation and swelling, further alleviating discomfort. Regular sessions can prevent future injuries by maintaining optimal muscle health and promoting better body mechanics, ultimately supporting overall musculoskeletal wellness.
Benefits of Soft Tissue, Deep Tissue, and Sports Massage:
Reduces muscle tension and soreness
Enhances flexibility and range of motion
Speeds up recovery from injuries
Improves circulation and blood flow
Reduces stress and promotes relaxation
Alleviates chronic pain
Prevents injury by targeting overworked Muscles
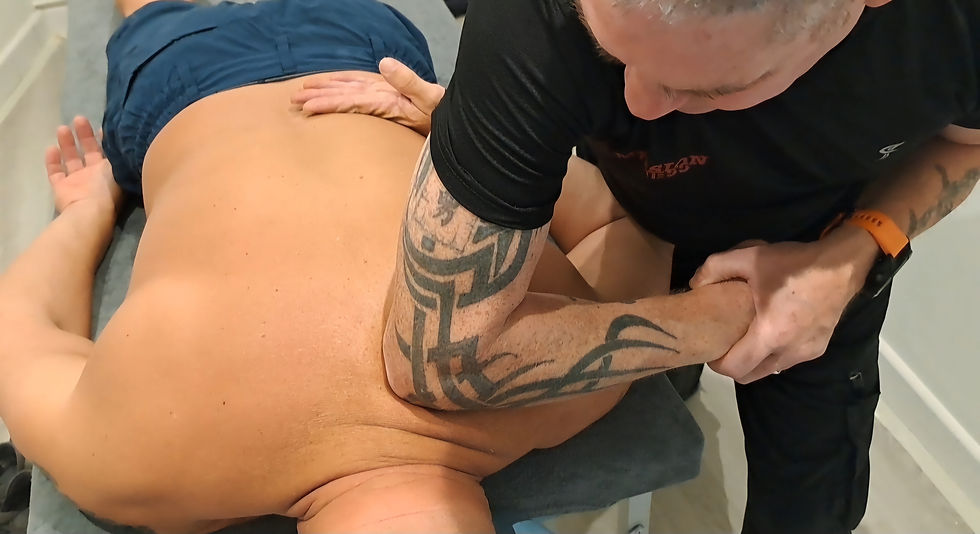
1: Soft Tissue
Massage
Soft tissue therapy involves the treatment of muscles, tendons, and ligaments to relieve pain, improve mobility, and aid recovery.
Deep tissue massage focuses on applying firm pressure to reach deeper layers of muscle, targeting knots, chronic tension, and muscle stiffness. It's particularly useful for conditions like back pain or postural problems.
Sports massage, on the other hand, is designed for athletes and active individuals. It combines deep tissue techniques with stretching to prevent injuries, enhance performance, and reduce muscle soreness after activity.
Both methods help improve circulation, reduce inflammation, and promote faster healing of soft tissue injuries.

2: Deep Tissue
Massage
Deep tissue massage is a technique that targets deeper layers of muscles and connective tissues to relieve chronic pain and muscle tension.
By using slow, firm pressure, it improves circulation, reduces inflammation, and alleviates stiffness.
Benefits include enhanced mobility, stress relief, and long-term pain reduction for improved overall well-being.

3: Sports
Massage
Sports massage is a therapeutic practice targeting muscles used in athletic activities and everyday movement.
It enhances blood flow, reduces muscle tension, aids in injury prevention, and accelerates recovery.
Benefits include improved flexibility, reduced soreness, and enhanced mental relaxation, supporting both athletes and everyday individuals in staying active and pain-free.

4: Pre/Post Sports
Massage
Pre-sports massage warms up muscles, increasing blood flow and flexibility, which enhances performance and reduces injury risk.
Post-sports massage aids recovery by flushing out toxins, reducing muscle soreness, and improving circulation to speed up healing.
Together, they support peak performance, quicker recovery, and help prevent future injuries.

5: Maintenance
Massage
A regular maintenance massage helps prevent muscle tightness, reduces stress, and improves flexibility.
By addressing minor aches before they escalate, it promotes long-term physical wellness.
Routine massages also enhance blood circulation and aid in faster recovery from physical activities, making it easier to sustain a balanced, active lifestyle.
-
How long does a functional movement assessment take?A typical assessment takes 60 minutes, depending on the complexity of the movements being tested and the individual's needs.
-
What are the key movement patterns tested?Common movement patterns include: Squatting Lunging Pushing and pulling Rotating or twisting Gait (walking or running) Balance and core stability
-
What can a functional movement assessment reveal?It can reveal: Muscle imbalances or weaknesses. Joint restrictions or poor mobility. Poor coordination or motor control. Potential injury risks.
-
How often should I have a functional movement assessment?Frequency depends on your goals: Athletes or active individuals may benefit from quarterly assessments. During rehabilitation, assessments may occur more frequently. For general fitness, annual check-ins can track progress.
-
Do I need to prepare for a functional movement assessment?Preparation involves: Wearing comfortable sports wear, preferably shorts and for ladies a sports bra. Being ready to perform basic movements like squats or lunges. Informing the assessor about any injuries or pain beforehand.
-
Can a functional movement assessment improve athletic performance?Yes, it helps athletes by: Identifying and correcting inefficient movement patterns. Reducing the risk of sports-related injuries. Enhancing strength, speed, and agility through targeted training.
-
What is a functional movement assessment?A functional movement assessment is a series of tests used to evaluate how well your body performs basic movement patterns. It helps identify imbalances, weaknesses, or mobility issues that could lead to pain or injury.
-
Why is a functional movement assessment important?Functional movement assessments are crucial for: Identifying movement dysfunctions that may lead to injury. Creating personalized exercise or rehabilitation plans. Improving overall performance in sports or daily activities. Enhancing posture, strength, and mobility.
-
Who can benefit from a functional movement assessment?Anyone can benefit, including: Athletes aiming to enhance performance. Individuals recovering from injury or surgery. People with chronic pain or mobility issues. Those starting a new fitness program.
-
How is a functional movement assessment performed?I will guide you through specific movements or exercises while observing your posture, range of motion, and control. I may also use tools like video analysis or markers to measure your performance.
-
Are there any side effects or risks?Soft tissue massage is generally safe, but mild side effects like temporary soreness or fatigue may occur. Avoid massage if you have open wounds, fractures, or certain medical conditions (e.g., blood clots) without consulting your doctor.
-
Can soft tissue massage help with injuries?Yes, it can aid recovery by: Reducing inflammation. Breaking down scar tissue. Restoring flexibility and range of motion. Enhancing blood flow to injured areas.
-
What is soft tissue massage, and how is it different from other massage types?Soft tissue massage focuses on the muscles, tendons, ligaments, and fascia to relieve pain, improve mobility, and aid recovery. It includes various types like deep tissue massage (for chronic tension), sports massage (targeting athletic performance), and maintenance massage (for ongoing care).
-
Who can benefit from soft tissue massage?Athletes (for performance and recovery). Office workers (to relieve postural strain). Individuals recovering from injury or surgery. Anyone experiencing muscle tension, pain, or stiffness.
-
What is deep tissue massage, and who is it for?Deep tissue massage uses firm pressure to release tension in deeper layers of muscle and fascia. It’s ideal for: Chronic pain or tightness. Postural issues. Recovery from injuries like strains or overuse conditions.
-
What is maintenance massage, and how often should I get one?Maintenance massage is regular treatment to keep muscles healthy, reduce stiffness, and prevent injuries. The frequency required depends on your activity level and needs, but athletes or highly active individuals often benefit from sessions every 2–4 weeks.
-
What is sports massage, and how does it benefit athletes?Sports massage is designed for athletes to: Enhance performance by reducing muscle tension. Prevent injuries through improved flexibility. Aid recovery by promoting circulation and reducing soreness.
-
How long does a session last, and what should I expect?A session typically lasts 1hr. Expect: An initial consultation to discuss concerns or goals. Techniques like kneading, stretching, and trigger point release. Adjustments based on your comfort and feedback during the session.
-
Is soft tissue massage painful?While deep tissue or sports massage may involve discomfort when addressing tight areas, it should not be unbearable. A skilled therapist will adjust pressure to your tolerance and ensure the treatment is effective yet comfortable.
-
What’s the difference between pre-sports and post-sports massage?Pre-sports massage: Uses fast, stimulating techniques to warm up muscles, improve circulation, and prepare the body for activity. Post-sports massage: Focuses on calming muscles, reducing soreness, and accelerating recovery after intense physical activity
-
What should I expect during a rehabilitation session?A session may include: Initial assessment to track progress. Guided exercises targeting the injured area. Manual therapy to reduce tension or improve mobility. Education on activity modifications and self-care.
-
Can I do injury rehab at home?Some rehab exercises can be done at home, but professional guidance is crucial to ensure exercises are performed correctly and safely. Regular check-ins with a therapist can optimise recovery.
-
What are the common phases of rehabilitation?Acute Phase: Managing pain and inflammation. Subacute Phase: Restoring mobility and strength. Rehabilitation Phase: Functional training and advanced exercises. Return-to-Activity Phase: Gradual reintroduction to normal activities or sports.
-
Can injury rehabilitation help with chronic pain?Yes, rehabilitation can be effective for managing chronic pain by: Improving joint mobility and muscle strength. Reducing stress on affected areas. Teaching proper movement patterns and pain management strategies.
-
Why is injury rehabilitation important?Rehabilitation helps: Speed up recovery. Restore normal movement and strength. Prevent future injuries. Reduce pain and inflammation.
-
What is injury rehabilitation?Injury rehabilitation is a process aimed at restoring strength, mobility, and functionality after an injury. It often includes physical therapy, exercises, and other treatments to promote healing and prevent further damage.
-
How long does injury rehabilitation take?The timeline varies based on the injury's severity and type. Minor injuries may require a few weeks, while severe injuries, such as fractures or ligament tears, may take months to fully recover.
-
How can I prevent re-injury during rehabilitation?Follow your therapist's recommendations. Avoid pushing through pain. Focus on proper form and technique. Gradually increase intensity and load. Warm-up and cool down effectively.
-
What treatments are used in injury rehabilitation?Common treatments include: Physical therapy exercises. Stretching and strengthening routines. Manual therapy (e.g., massage, joint mobilisations). Modalities like heat, ice, or ultrasound. Education on posture and ergonomics.
-
When should I start injury rehabilitation?Rehabilitation often starts immediately after an injury, focusing on pain control and gentle movement. Delaying treatment can lead to stiffness, weakness, or chronic pain.
-
Can I do post-op rehab at home?While some exercises can be done at home, professional guidance ensures proper technique and prevents re-injury. Regular sessions with a therapist are often recommended during the initial stages.
-
When should I start post-op rehab?The timing depends on the type of surgery. For some procedures, rehab starts within a day or two, focusing on gentle movement. In other cases, it may begin weeks later, once healing has progressed.
-
What are the risks of skipping post-operation rehab?Without rehab, you risk: Prolonged pain and swelling. Loss of strength, mobility, and function. Development of scar tissue or stiffness. Increased likelihood of re-injury or complications.
-
What is post-operation rehabilitation?Post-operation rehabilitation is a structured recovery program designed to help patients regain strength, mobility, and function after surgery. It includes physical therapy, exercises, and treatments tailored to the specific surgery and individual needs.
-
What does a typical post-operation rehab program include?Programs vary but may include: Physical therapy exercises. Manual therapy to improve mobility. Pain management techniques. Education on proper posture and movement. Guidance on gradually resuming daily activities.
-
How can I speed up my recovery during rehab?Follow your therapist’s instructions diligently. Stay consistent with prescribed exercises. Eat a healthy diet to support healing. Avoid overexertion and listen to your body. Stay positive and patient—recovery takes time.
-
How long does post-operation rehabilitation take?The duration depends on the type and complexity of the surgery. Minor procedures may require a few weeks of rehab, while major surgeries, such as joint replacements, may need several months.
-
Will rehabilitation be painful?Some discomfort is normal, especially when working on stiff or weak areas. However, therapy should not cause severe pain. As your therapist, I will adjust the intensity to your comfort level.
-
What surgeries commonly require rehabilitation?Rehab is commonly needed after: Orthopedic surgeries (e.g., knee or hip replacements, rotator cuff repairs). Spinal surgeries. Cardiac surgeries. Abdominal surgeries. Sports-related surgical procedures.
-
Why is post-operation rehabilitation important?Rehabilitation is crucial for: Restoring strength and range of motion. Reducing pain and swelling. Preventing complications like stiffness or scar tissue. Helping patients return to daily activities safely.